October 5, 2015
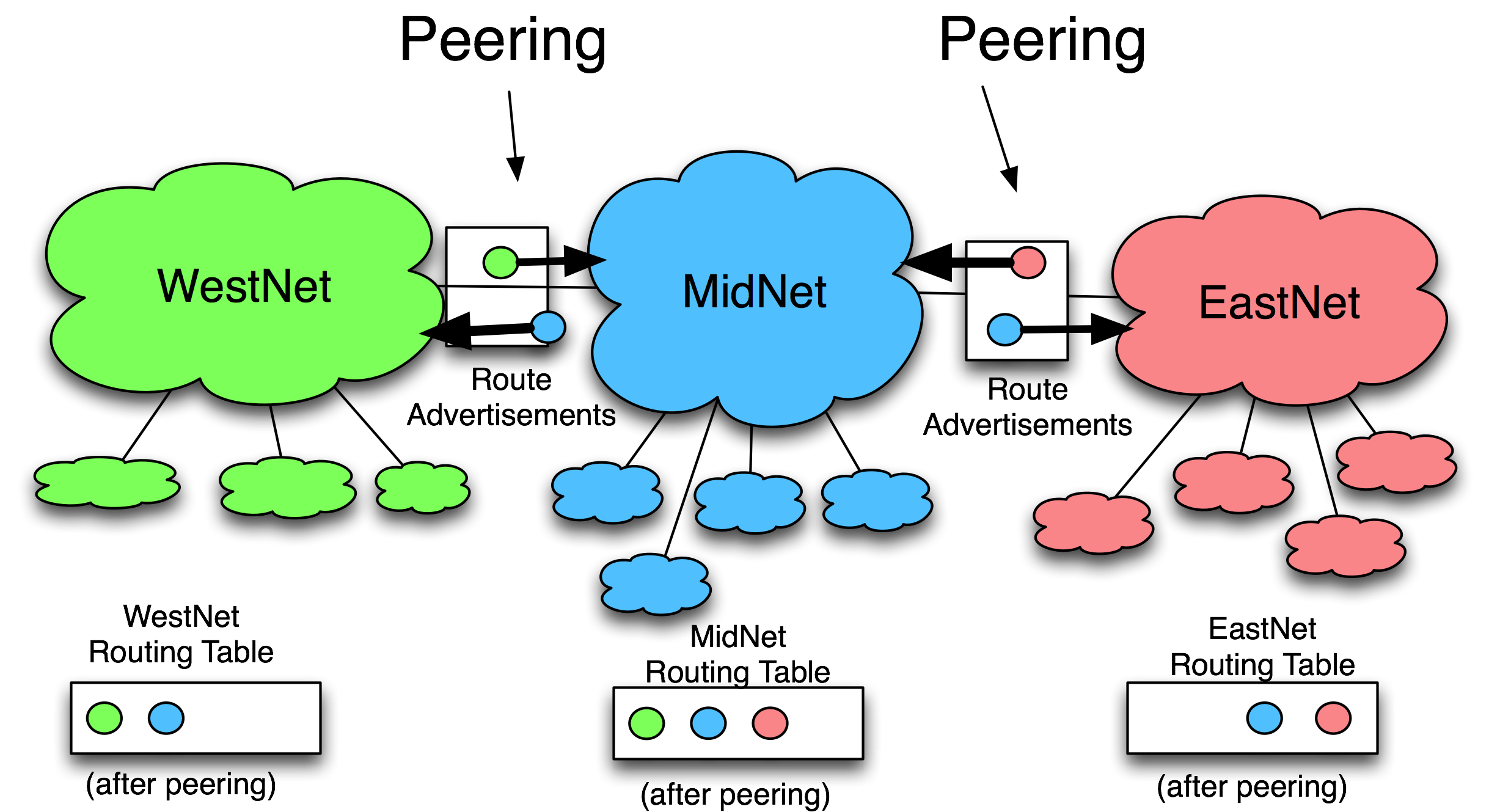
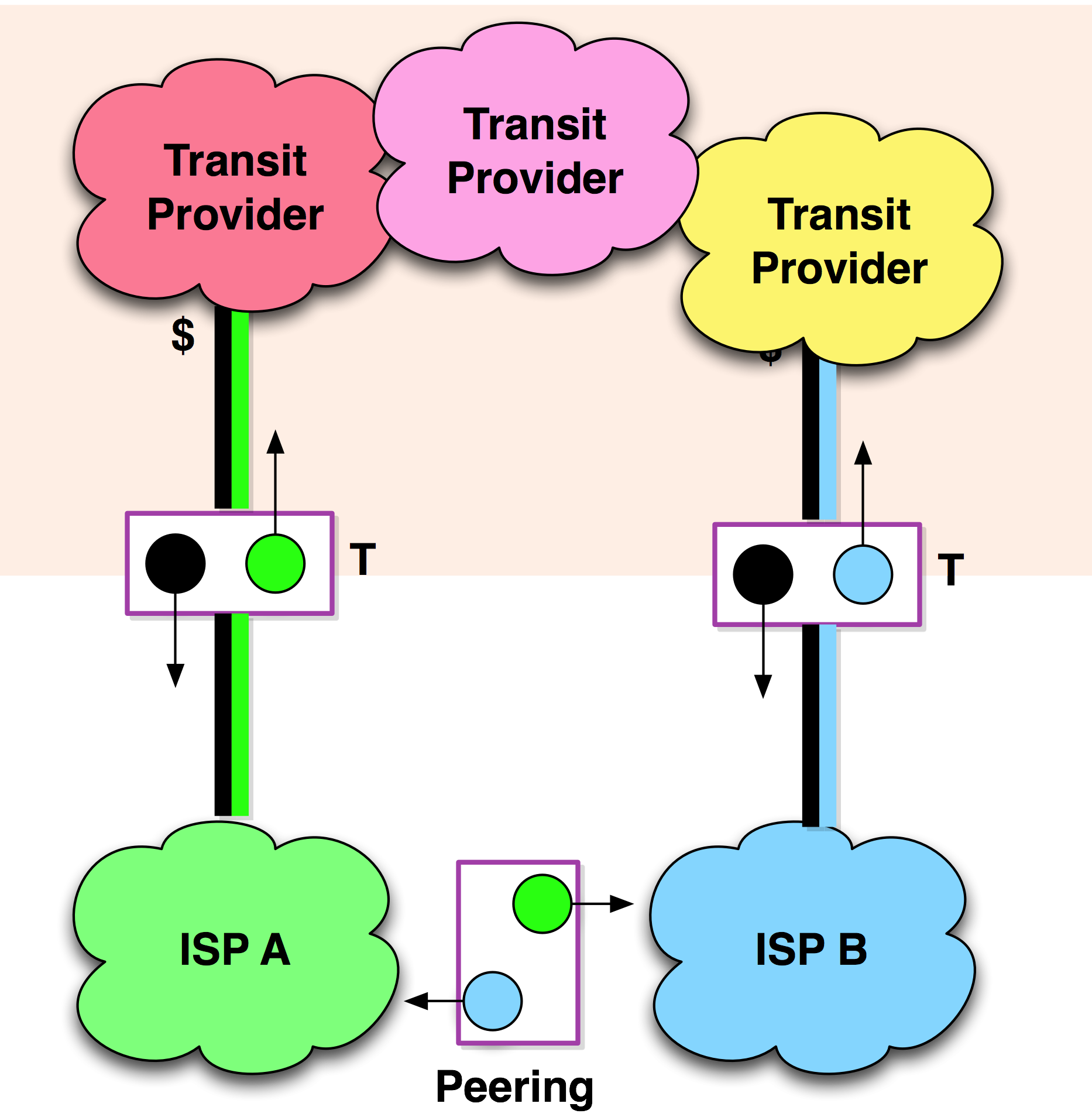
There is a lot of talk on peering for internet. Here is a link that will help us clarify our terms and understanding of internet peering
Definition of Internet Peering
Some of the key points on internet peering:
1. There is no substitute for transit exchanges (the main nodes)
2. Internet peering is settlement free. Thus two exchanges will not pay one another because they just exchange use of facilities. Thus if PLDT and Globe goes on peering, neither pays each other fees. These leads to lower cost. PLDT thus would object to this because it means loss of revenues. Thus all the smokescreen by spokesmen and the head of the dominant Telco, is about protection of revenues
It is all about making more money and about supporting the nation and its citizens. Quo vadis telcos?
So as it is there is no direct traffic between Globe and PLDT. All traffic goes to the intl gateway adding to costs and time, and thus slower speed
3. It is not a transitive relationship
Reasons for peering
1. Costs reduced (because there is no cost payment between two exchanges eg between Globe and PLDT
2. Revenues are increased because of faster access and more access
3. Routing can be made strategic; local traffic can be only routed direct, and intl traffic can be through an exchange. Private exchanges purely dedicated to internet traffic are the norm in other countries
4. Customer experience is enhanced
Peering from Wiki

No comments:
Post a Comment